Hormones and weight loss are tightly connected. These chemical messengers decide how your body burns calories, stores fat, and regulates hunger. If they’re out of balance, fat loss becomes an uphill battle. In this guide, we’ll break down the real science behind hormones, fat storage, and practical steps to get results without gimmicks.
Table of Contents
Hormones and Their Role in Weight Loss
Understanding Hormonal Imbalance in Fat Loss
Hormonal imbalance fat loss challenges show up as stubborn fat, fatigue, or cravings that don’t match your calorie intake. Leptin resistance can trick the brain into believing you’re starving. Thyroid slowdown reduces energy burn. Cortisol from stress locks fat around the belly. Understanding these signals is the first step toward fixing them.
Key Female Weight Loss Hormones
Female weight loss hormones include estrogen, progesterone, thyroid hormones, leptin, and ghrelin. Estrogen supports healthy fat distribution, while low estrogen encourages belly fat. Progesterone fluctuations affect water retention and cravings. Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism speed. Leptin signals satiety, while ghrelin stimulates hunger. When these hormones swing out of balance, weight control becomes more difficult.
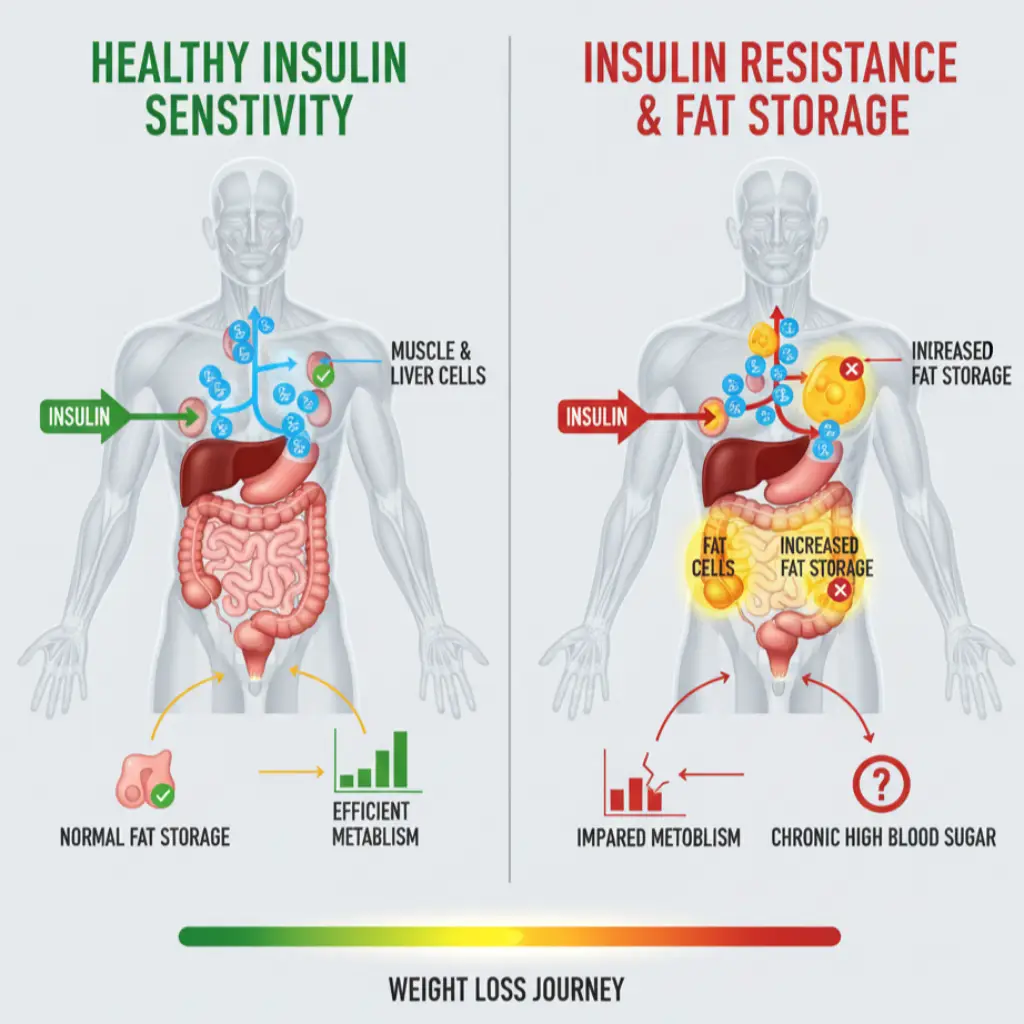
Insulin Resistance and Weight Loss
Insulin and Fat Storage
Insulin is one of the strongest fat storage hormones. After meals, insulin clears glucose from the blood. When resistance develops, blood sugar spikes, and the body stores more fat—especially in the belly. Insulin resistance and weight loss problems go hand in hand because the body struggles to burn stored fat efficiently.
Resetting Insulin Sensitivity Through Nutrition
Improving insulin sensitivity is possible through balanced eating. Whole foods, protein with each meal, and fiber slow glucose spikes. Avoiding constant snacking allows insulin to rest. Exercise, especially resistance training, also helps muscles use glucose effectively. For more guidance, see our guide on Sustainable Calorie Deficit.
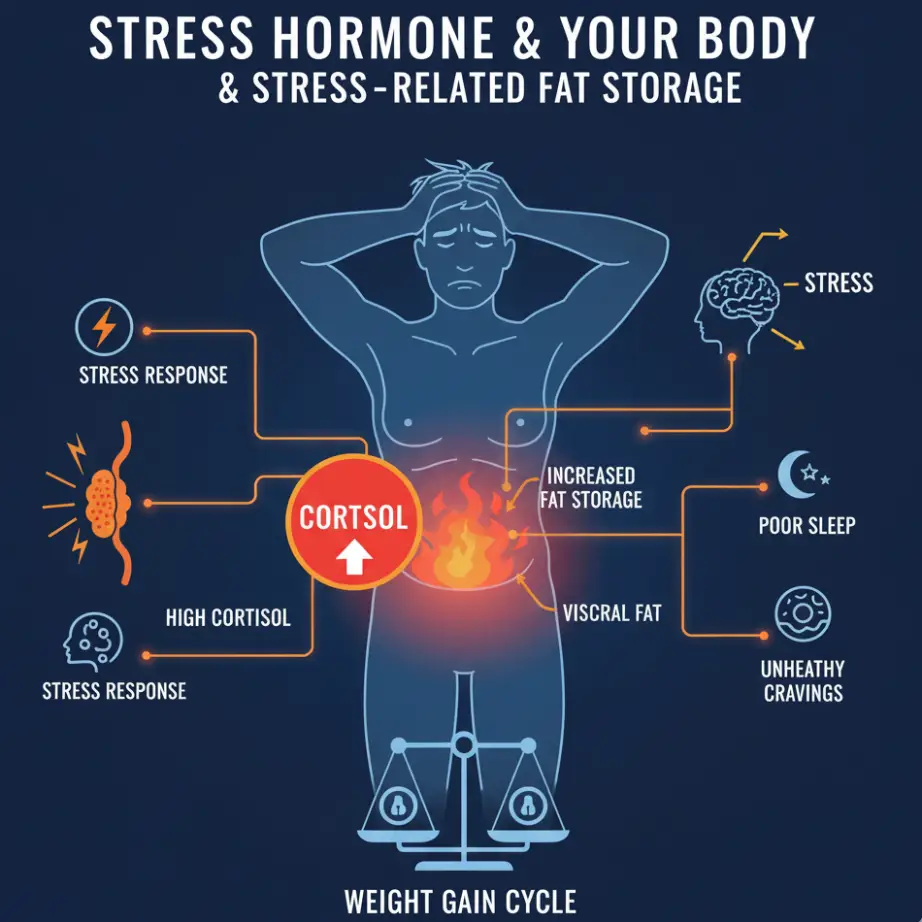
Cortisol and Fat Storage
Stress Hormones and Belly Fat
Cortisol and fat storage are closely linked. Chronic stress elevates cortisol, signaling the body to hold fat around the midsection. This fat is particularly harmful because it surrounds organs, raising disease risk. Over time, cortisol imbalance makes fat loss difficult despite good nutrition.
Reducing Cortisol for Better Fat Loss
Reducing cortisol involves more than avoiding stress. Consistent sleep, adequate protein, proper hydration, and recovery days all play a role. Mindfulness techniques such as breathing and journaling also lower cortisol response. Building supportive routines is key—learn more in our Mindset and Habit Building guide.
Estrogen, Progesterone, and Female Weight Loss
Rapid Weight Loss and Estrogen Levels
Crash diets quickly lower estrogen. In women, this can cause irregular cycles, bone density loss, and mood shifts. Estrogen also affects muscle recovery, so very low levels can stall training progress. Rapid weight loss hormone imbalance often rebounds into fat gain once normal eating resumes.
Balancing Female Hormones for Sustainable Fat Loss
Balanced nutrition, strength training, and consistent sleep support female weight loss hormones. Resistance training helps preserve estrogen’s role in fat distribution and lean mass. Moderate-intensity cardio also supports heart health without overly suppressing hormones. Learn more about the Role of Strength Training in Fat Loss.
6 Fat-Burning Hormones Explained
Growth Hormone, Thyroid, Leptin, Ghrelin, Adiponectin, and Testosterone
These six fat-burning hormones control how the body mobilizes and burns fat:
- Growth Hormone: boosts fat breakdown during sleep and fasting.
- Thyroid Hormones: regulate calorie burn.
- Leptin: signals fullness.
- Ghrelin: triggers hunger.
- Adiponectin: improves fat metabolism and insulin sensitivity.
- Testosterone: supports muscle growth and fat burning.
Practical Ways to Support These Hormones Naturally
Supporting these hormones means following consistent basics:
- Prioritize sleep for growth hormone release.
- Eat adequate protein and iodine-rich foods for thyroid health.
- Train with resistance and compound lifts for testosterone.
- Avoid extreme diets to keep leptin and ghrelin balanced.
For structured methods, see Combining Cardio and Strength Training.
Hormonal Weight Gain: Causes and Signs
Signs of Hormonal Weight Gain
Hormonal weight gain shows up as stubborn belly fat, fatigue, low mood, and poor recovery. Constant cravings, irregular cycles in women, and difficulty losing weight even with diet adjustments may also appear.
How to Stop Hormonal Weight Gain
Stopping hormonal weight gain requires addressing the root cause. Adjusting meal quality, sleep patterns, and stress management works for most. Sometimes medical conditions like hypothyroidism or PCOS need professional care. For a deeper dive into possible blocks, check Why You’re Not Losing Weight.
Resetting Hormones for Fat Loss
How to Reset Female Hormones for Weight Loss Naturally
Female hormones respond well to gradual, consistent changes. Whole foods, quality protein, and omega-3 fats balance hormone production. Lifting weights helps normalize estrogen and progesterone shifts. Avoiding chronic stress supports thyroid and adrenal balance.
Supplements to Balance Hormones and Lose Weight
Some supplements help when used responsibly:
- Vitamin D for thyroid and immune health
- Magnesium for cortisol balance
- Omega-3 fatty acids for insulin sensitivity
- Adaptogens like ashwagandha may lower cortisol in stressed individuals
Avoid quick-fix products. Supplements support a lifestyle but do not replace it. For building sustainable results, see Long-Term Fat Loss Lifestyle.
Hormones, Rapid Weight Loss, and Long-Term Body Goals
Rapid Weight Loss Hormone Imbalance Risks
Rapid weight loss leads to thyroid suppression, increased cortisol, reduced leptin, and higher ghrelin. The body responds by slowing metabolism and increasing hunger, creating rebound fat gain. This is why crash diets rarely succeed long term.
Setting Healthy Hormonal Fat Loss Goals
Healthy fat loss goals focus on steady progress, not speed. Building lean muscle improves hormonal balance and long-term fat control. The best results come from focusing on body composition, not just scale weight. For motivation, check out Healthy Six-Pack Goals and Before and After Transformations.
| Hormone | Effect on Weight Loss |
|---|---|
| Insulin | Controls blood sugar, excess leads to fat storage. |
| Cortisol | High levels store belly fat and increase cravings. |
| Estrogen | Supports lean mass and fat distribution; low levels promote belly fat. |
| Leptin | Signals fullness; resistance causes overeating. |
| Thyroid Hormones | Regulate metabolism and calorie burn. |
Conclusion
Hormones and weight loss are inseparable. Insulin, cortisol, estrogen, and other hormones determine how easily your body burns fat. Crash diets create hormonal chaos, while sustainable nutrition, training, and lifestyle balance reset them naturally. Build long-term habits instead of chasing quick fixes, and your hormones will work with you, not against you.
FAQs
Female hormones weight loss
Estrogen, progesterone, and thyroid hormones strongly influence weight control in women. Balanced levels help regulate appetite, fat distribution, and energy use.
Signs of hormonal weight gain
Unexplained belly fat, cravings, fatigue, low mood, and irregular cycles are common. These signs may suggest insulin resistance, cortisol imbalance, or thyroid slowdown.
How to reset female hormones for weight loss naturally
Consistent exercise, stress management, and nutrient-dense foods reset female hormones naturally. Adequate sleep is also critical.
Rapid weight loss and estrogen levels
Crash diets lower estrogen, disrupting cycles and increasing rebound fat storage. Long-term health requires steady weight loss instead.
Supplements to balance hormones and lose weight
Vitamin D, magnesium, and omega-3s support hormone balance. They should complement, not replace, nutrition and exercise.
6 fat-burning hormones
Growth hormone, thyroid, leptin, ghrelin, adiponectin, and testosterone regulate fat burning and appetite.
Rapid weight loss hormone imbalance
Quick fat loss increases cortisol, reduces thyroid activity, and disrupts leptin. These shifts slow metabolism and trigger rebound.
How to stop hormonal weight gain
Prioritize balanced meals, strength training, and stress reduction. Seek medical advice if hormonal conditions like hypothyroidism are suspected.
Visit my Instagram account for more
